The Gold Standard
Breast milk is considered as the gold standard for infant development and health.
When infants cannot be solely breastfed, safe and nutritious alternatives that are compositionally or functionally close to breast milk need to be provided.
Unique Oligosaccharides
HMOs (Human Milk Oligosaccharides) are a complex family of carbohydrates naturally occurring in human breast milk and represent the third most abundant solid components after lactose and lipid. More than 200 different HMOs are identified in human milk. Each HMOs has lactose as the core building block. By elongation and branching of lactose with 5 different simple sugars, glucose, galactose, N-Acetyl-Glucosamine, fucose or N-Acetyl-Neuraminic Acid (sialic acid), each HMO has a unique structure.

HMO Structures
The following list shows the typical 23 species of HMOs that have already been reported in published literatures. 180 species of HMOs have been structurally determined.(as of August 2023)

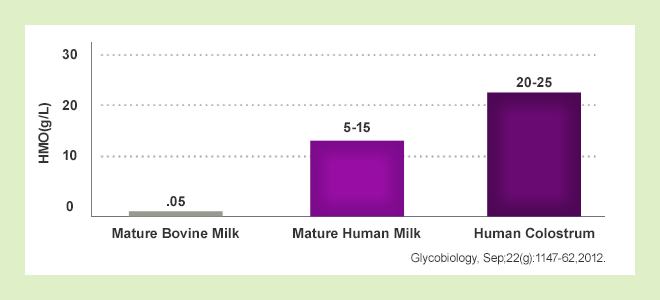
HMOs Concentration in the breast milk
HMOs are the key components that distinguish human milk from other mammalian milk. HMOs are particularly abundant in human colostrum while bovine milk contains little or trace amounts of HMOs. [1]
Functions of HMO
Prebiotics
HMOs are not digested in the intestine and most of the ingested HMOs reach the large intestine to work as prebiotics*, the food for beneficial bacteria in the gut. HMOs are known to support a development of healthy microbiome of infants.[3]

*What is the Prebiotics?
Prebiotics is defined by The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) that “a substrate that is selectively utilized by host microorganisms conferring a health benefit.”[4]
Contribution to Immune System
Structures of HMOs resemble the receptors on the cells that pathogens adhere to get access to human body.[1] It is estimated that more than 40 % of consumed HMOs are eliminated from the gut. HMOs may help remove the pathogens from the body to establish an environment for beneficial bacteria to grow. [3]

References
- Hundshammer C, Minge O. In Love with Shaping You---Influential Factors on the Breast Milk Content of Human Milk Oligosaccharides and Their Decisive Roles for Neonatal Development. Nutrients. 2020;12.
- Bode L. Human milk oligosaccharides: every baby needs a sugar mama. Glycobiology. 2012;22 9: 1147–1162.
- Zhang S, Li T, Xie J, Zhang D, Pi C, Zhou L, et al. Gold standard for nutrition: a review of human milk oligosaccharide and its effects on infant gut microbiota. Microb Cell Fact. 2021;20: 108.
- Gibson GR, Hutkins R, Sanders ME, Prescott SL, Reimer RA, Salminen SJ, et al. Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of prebiotics. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;14: 491–502.















